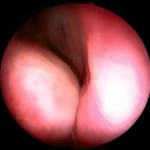
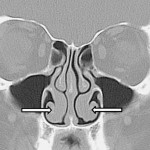
Turbinates are structures within the nose that protrude towards the airway from the nasal sidewall. Most people have three pairs of nasal turbinates, some have four. It is the lower (i.e. inferior) turbinate that is usually addressed with turbinate surgery. The middle turbinates play a role for the nasal sinuses and therefore, they are sometimes modified during sinus surgery. Turbinates are bony structures covered by moist mucosa. Turbinates provide important functional benefits for normal nasal hygiene by moistening, warming and cleaning the air that flows into the nose. Therefore, removal of turbinates is usually not an appropriate treatment for their enlargement.
Candidacy for Inferior Turbinate Surgery
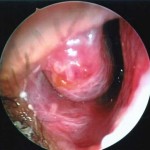
The inferior turbinates are by far the largest of the three (or four). If they become abnormally enlarged the turbinates may contribute to nasal obstruction. For instance, when we have a cold or nasal allergy, the turbinates swell and produce excessive fluid leading to nasal blockage. Rarely though, their size is the only reason for obstructed nasal breathing. Therefore, reduction of the turbinate size (turbinoplasty) is commonly performed in conjunction with septoplasty. When the septum is deviated to one side, the turbinate of the other side may become larger (compensatory inferior turbinate enlargement or hypertrophy). Unless this enlarged turbinate is reduced, straightening of the septum may now lead to obstruction of the nasal airway by the enlarged turbinate structure. In addition, if certain nasal conditions do not respond well to medical treatment, your physician may recommend turbinoplasty.
How is an Inferior Turbinoplasty Performed?
Various procedures have been designed for turbinoplasty. A small inside incision may be placed and the turbinate bone can be removed with special instruments. Alternatively, the bone can be crushed in order to convince the turbinate not to stick too far into the nasal sidewall. The fleshy cover of the bone can be reduced by excision or with the help of heat. In general, the goal is a gentle reduction in size, not a removal of the turbinate. Turbinoplasty is usually performed under conscious sedation (twilight sleep) or general anesthesia.
Turbinoplasty with shaver pdf article
- Alerginis rinitas
- Vazomotorinis rinitas
- Vazomotorinis rinitas. Sinusu KT
- Hipertrofinis rinitas
Nasal tampons types: gauze, soft tampons
Removal of nasal tampons
Radiofrequency reduction of inferior turbinates
Radiofrequency reduction of inferior turbinates with Cellon
Radiofrequency reduction of inferior turbinates with Ellman RF
Reduction of inferior turbinates with shaver